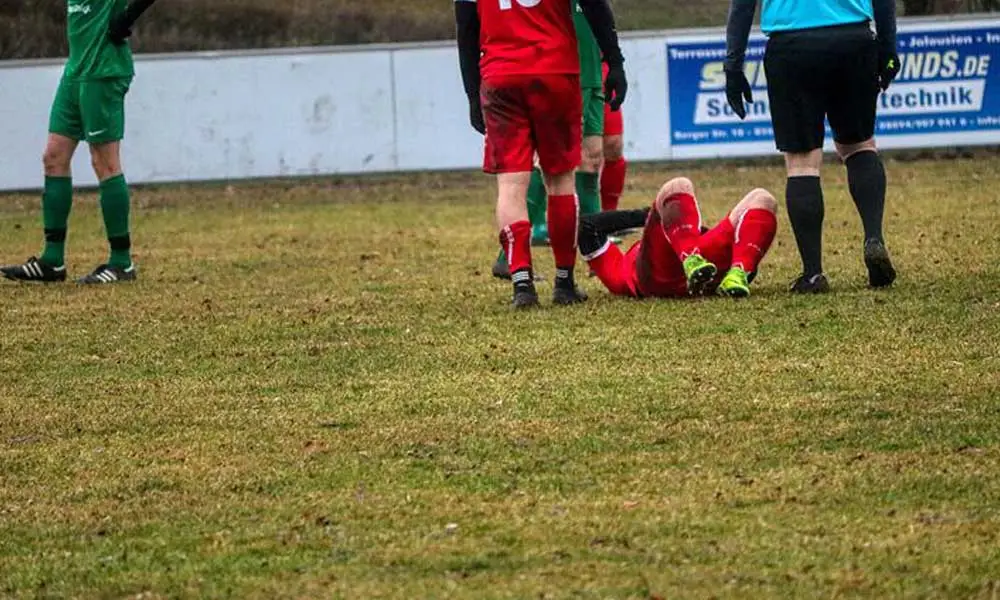
Being physically active is an important component of any healthy lifestyle, yet playing sports and working out can sometimes result in injuries. Injuries can result from accidents, inadequate training, improper stretching, and inappropriate equipment, among other things.
Those who are most vulnerable are:
Individuals who have been inactive for a long time
Those who workout without warming up or stretching
Those who engage in action or contact sports, such as snowboarding or mountain biking
Excessive activity without sufficient downtime
What Kinds of Sports Injuries Occur Most Frequently?
Depending on their severity, sports injuries can cause a wide range of symptoms and problems. Sports injuries are frequent and include:
- Sprains or Ligament Injuries – an injury to a ligament, the connective tissue between bones, such as a stretch, twist, or rupture. The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL), the elbow’s ulnar collateral ligament (UCL or Tommy John injury), and ankle sprains are all common ligament ailments.
- Strains are defined as a strain, twist, or tear in a tendon or region of muscle, which is a robust, fibrous tissue that joins muscles to bones. Mild ankle sprains or strained muscles are examples of common strains.
- Muscle, ligament, or tendon trauma or damage is referred to as a soft tissue injury.
- Sprains, strains, bursitis, dislocations, fractures, meniscus tears, ligament tears, and overuse injuries can all occur in the knee.
- Muscular swelling and soreness can be brought on by impact or strain, as well as by new activity and muscle development.
- Achilles tendon rupture or tear – If overstretched, this big tendon in the lower leg can sustain damage or rip.
- Dislocations are joint injuries where a bone is forced out of its socket. The injury causes pain, swelling, and immobility in the injured area.
- In most cases, a high-force impact or other stress on the bone causes fractures, which can be minor cracks or even completely broken bones.
- Injuries to the muscles and tendons that surround the shoulder joint and attach to the humerus are referred to as rotator cuff injuries.
Are injuries caused by sports treatable?
The ‘P.R.I.C.E’ approach can be used to treat minor sports injuries.
Protection. After an injury, protect the area from more injuries and infections.
Rest. Allow your body to heal. Taking some time off is very important.
Ice. Ice helps control pain and swelling.
Compression. Compression helps limit swelling of the injured area.
Elevation
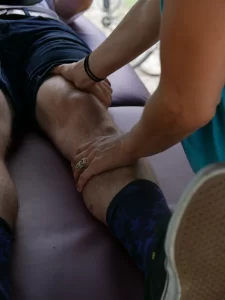
This can aid in reducing pain and swelling when combined with basic pain management modalities such as cryotherapy, Electro therapy, etc.
What if your symptoms sustain?
Seek medical attention right away for sports injury therapy if any of the following symptoms are being brought on by your sports injury. An immediate assessment by a sports medicine expert can aid in the diagnosis of your issue and put you on the path to recovery.
Extreme ache or swelling
Body limb anomalies
Any unusual noises, such as popping or crunching, extreme lassitude, or immobility in the afflicted area
Dizziness
Having trouble breathing
Fainting or collapsing
Muscle Pull
A pulled muscle is also referred to as a muscle strain. When a muscle is stretched too far, it tears. Among the signs of a pulled muscle are:
pain
swelling
fragility and
incapacity or trouble in using the muscle.
The most typical locations for pulled muscles include the quadriceps, calf, hamstrings, groin, low back, and shoulder.
Strains
Strains are by far the most prevalent of all sports-related injuries simply because we use so many muscles and tendons when we exercise or play. All of these moving parts are prone to stretching further, which can cause pain, damage, and tearing. Hamstring, groin, and quad strains are a few examples of common muscle injuries. The majority of sprains are minor and naturally disappear with rest. Before engaging in any strenuous exercise, it is best to warm up and stretch to lower the risk of strained muscles and tendons.
Sprains
Ligaments are the tissues that connect bone to bone. These ligaments may strain or tear if they turn in the wrong direction. Perhaps the most common type of sprain among athletes is the ankle, followed closely by the knee, wrist, elbow, etc. Sprains can hurt, take longer to recover than strains, and occasionally need to be immobilized to prevent further damage. Stretching and warming up before a workout can help prevent sprains, as can using proper technique in the sport you’re playing. If you have a history of spraining a joint, such as a knee or an ankle, it would be wise to support that joint with a brace while playing because sprains frequently leave the ligament weak and prone to future sprains.
Knee problems
We’ve assigned the knee its category for potential injuries because it’s a very intricate joint that experiences several impacts during most sporting activities. Along with cartilage rips, dislocations, and fractures, anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tears are fairly typical orthopedic injuries. Knee injuries are frequently treated with surgery since they can be extremely painful and debilitating. , Correct cushioning and bracing, coupled with warm-ups, stretches, and excellent posture can lower the risk of knee injury (for instance, while playing contact sports).
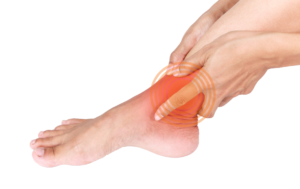
Fractures
Impact and contact sports frequently result in bone fractures (most commonly in the arms, legs, and feet), all of which can be painful, require weeks of immobility to heal, and are occasionally corrected surgically. Most demanding and/or contact sports carry an inherent risk of fractures, but you can lower it by using the right padding, warming up, exercising to keep your muscles strong and flexible, using proper technique, etc. Also, don’t “play through the pain,” as sometimes the pain is a sign of a strain or sprain that left untreated can make the bone vulnerable to fracture.
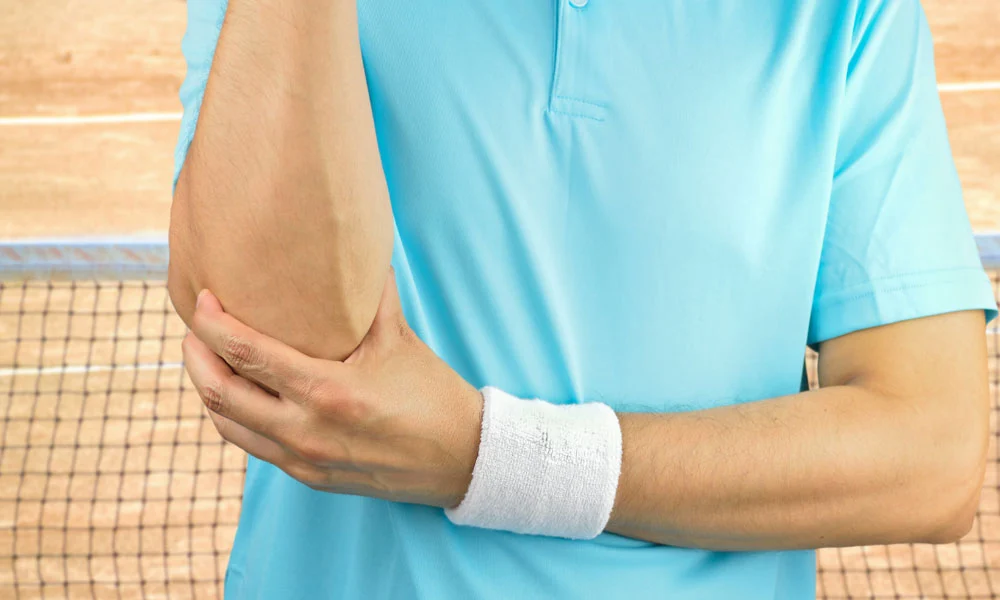
Tennis elbow
A tennis elbow can develop without playing the sport of tennis (golf is also a common culprit). Tennis elbow is one of many “injuries of repetition,” which are strained elbow ligaments brought on by excessive and repetitive use. Pace yourself if you want to avoid it. Take breaks, conduct other activities, and always warm up and stretch before playing.
Shin splints and plantar fasciitis
These conditions are categorized as repetitive stress injuries since they both involve excessive foot and leg movement coupled with inadequate support. An inflamed tendon in the foot’s arch is called plantar fasciitis, and it hurts to walk. Shin splints are a term used to describe an inflammation of the lower leg muscles brought on by constant strain and hard impacts from running, dodging, or abrupt stops and start. Both are typical among joggers, runners, soccer, and basketball players, etc. The two most effective preventatives are appropriate stretches and periodic rest.
Back pain or back injury
With almost every sport, your back and spinal column experience some level of stress. This stress may build up over time into inflammation around the vertebrae and back muscles, resulting in upper or lower back discomfort. Occasionally, a sudden, jarring hit can also seriously hurt the back. Depending on the problem, back treatments might range considerably from rest to physical therapy to surgery. The greatest method to lower your chance of back discomfort and injury is to maintain strong, flexible back muscles with frequent low-impact exercise, warm-ups, and even a healthy diet.
Concussion
A concussion, which is most frequent in contact sports like football, happens when the brain suddenly moves inside the skull after being struck, sometimes injuring the tissues that hold it there. Concussions can range in severity from moderate to severe, and their symptoms might include anything from headaches and vertigo to drowsiness and brief unconsciousness. Always get checked out by a spine-and-brain expert after a head injury since sometimes, afterward, more severe symptoms may appear. Never continue to play sports if signs of a concussion occur. With rest, concussions typically recover naturally within a week to several weeks. Wearing the proper protective headgear while engaging in contact sports like hockey or football, riding, skateboarding, etc. is the best approach to lower the risk of concussion.
How Can Injuries Caused by Sports Be Prevented?
In general, injuries can be avoided by utilizing good techniques, using the right equipment, following a healthy rest schedule, and stretching before and after activity.

However, since accidents can occur, it is best practice to wear the appropriate safety equipment, such as helmets, knee and elbow pads, gloves, and perhaps body armor for extreme sports that carry a higher risk of injuries.
Regular exercise is advised for several sports to reduce the risk of injury. In particular, this is valid for repetitive motion sports. Creating a sound strengthening and conditioning program can aid in avoiding aches and pains and injuries.
Athletes can receive expert care from Maana Health to heal from various sports injuries, including those to the spine, knee, muscles, joints, etc. To find out more, call +91 99950 89400.

